Inventory Management Systems
An inventory management system is a set of tools, software, and procedures companies apply to effectively control their inventory. A Closer Look at Top IMS Solutions for Businesses
How Inventory Powers Business Success
Inventory in business refers to the total stock of goods a company owns for sale or manufacturing. It is among a company's most precious assets and is very important for operational effectiveness, supply chain management, and customer satisfaction. Effective inventory control guarantees companies have the correct goods at the correct moment, therefore avoiding stock shortages and unnecessary storage expenditures.
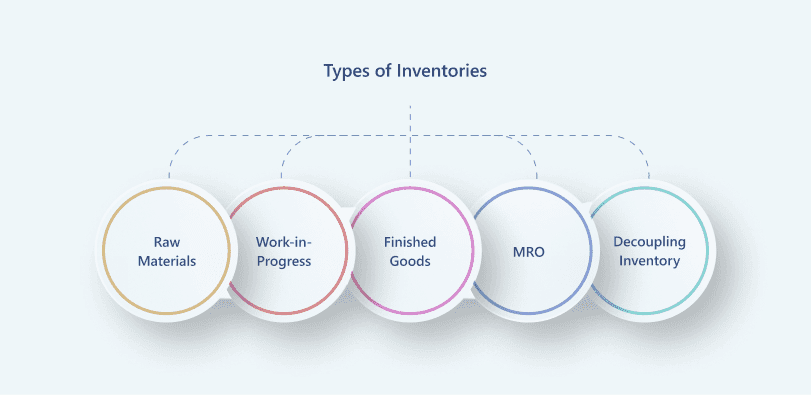
Types of Inventories
Based on its function in manufacturing and sales, inventory is essentially classified into several categories:
The deliberate process of obtaining, storing, tracking, and selling goods with a goal toward balancing supply and demand while lowering costs is known as inventory management. This entails:

An inventory management system is a set of tools, software, and procedures companies apply to effectively control their inventory. Real-time inventory control and visibility offers guarantees accuracy, automation, and efficient operations.
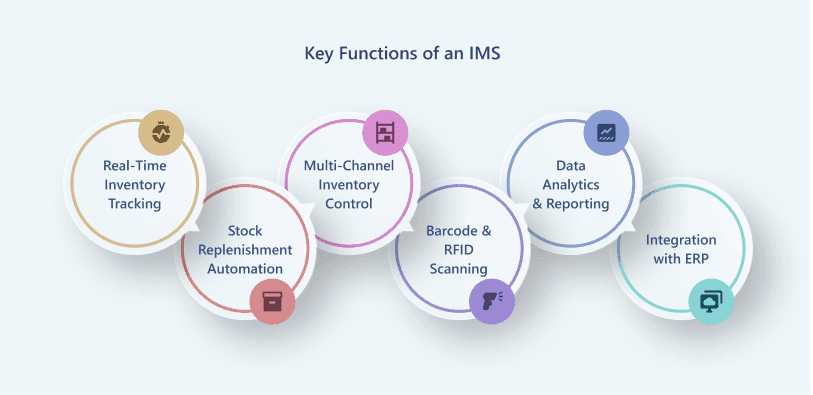
Key Functions of an IMS
A well-designed Inventory Management System typically includes:
In the upcoming sections, we’ll explore:
Exploring Inventory Management Systems.

Whether it's for sale, buy, or stock transfer, a perpetual inventory stock management systemautomatically changes inventory records with every transaction, preserving real-time stock updates. This method guarantees that companies always examine their inventory levels with accuracy and current.
How It Works:
Key Benefits:
Challenges:
A periodic inventory management system updates inventory records at fixed intervals, relying on physical stock counts rather than continuous tracking. The Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) is calculated only at the end of each period.
How It Works:
Key Benefits:
Challenges:
Installed on a company's internal computers, an on-premises inventory management system offers enterprises total control over data storage and security.
Important Characteristics:
Challenges:
A cloud-based inventory stock management system is hosted on external servers and accessed through the internet, offering real-time synchronization across multiple locations.
Key Features:
Challenges:
An on-premises inventory stock management system is installed on a company’s internal servers, giving businesses complete control over data storage and security.
Key Features:
Challenges:

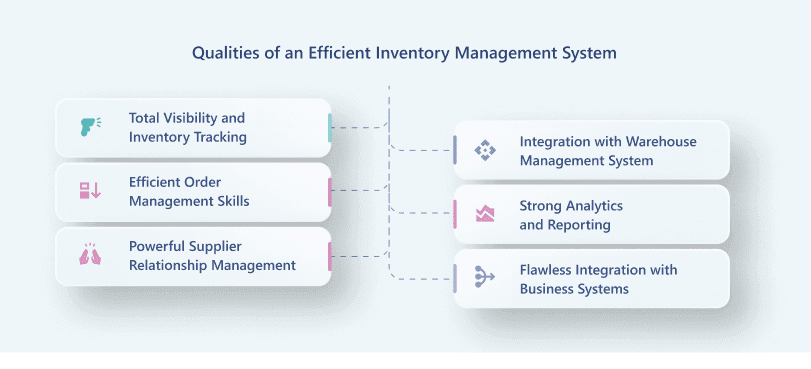
Required Abilities for Correct Tracking and Optimization
Real-time, multi-location inventory provided by inventory management systems guarantees companies can trace stock movements at every level:
An inventory management system software should guarantee smooth procurement, sales, and fulfillment of orders. To do this, it should have:
SRM tools included in the best inventory management system enable companies to monitor supplier performance and maximize procurement plans.
The best inventory management system should include WMS features for smooth digital and physical stock tracking for companies running large-scale warehouses.
The best inventory stock management system offers insights on demand forecasting, sales trends, and stock movements. This helps companies match demand with stock levels, therefore lowering holding expenses.
The best inventory stock management system offers insights on demand forecasting, sales trends, and stock movements. This helps companies match demand with stock levels, therefore lowering holding expenses.
An inventory management system software should interact with other vital business applications if it is operated at top efficiency:
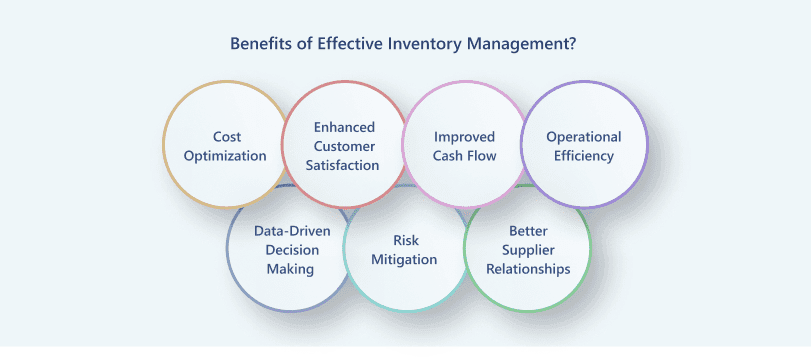
Cost Savings, Efficiency, and Improved Customer Satisfaction
Maintaining optimal inventory levels is essential to minimize costs associated with overstocking and stockouts. Excess inventory ties up capital and incurs storage expenses, while insufficient stock can lead to lost sales and expedited shipping costs. By implementing precise inventory control measures, businesses can balance supply with demand, reducing unnecessary expenditures and enhancing profitability.
Reliable inventory management ensures that products are available when customers need them, preventing stockouts that can damage customer trust and loyalty. Consistently meeting customer demand fosters a positive reputation and encourages repeat business, which is vital for long-term success.
Effective inventory management prevents overinvestment in stock, freeing up capital for other critical business operations. By accurately forecasting demand and maintaining appropriate stock levels, companies can improve the cash flow, allowing for better financial flexibility and investment opportunities.
Streamlined inventory processes reduce manual errors and labor costs, leading to more efficient operations. Automation in inventory management minimizes human intervention, accelerates workflows, and enhances accuracy in tracking and reporting.
Advanced inventory stock management system provides valuable insights into sales trends, stock levels, and consumer behavior. Access to real-time data enables businesses to make informed decisions regarding purchasing, marketing strategies, and resource allocation, ultimately driving growth and competitiveness.
Proper inventory management systems help identify and address potential risks such as theft, damage, or obsolescence. Implementing regular audits and monitoring inventory turnover rates can mitigate these risks, ensuring that the business maintains a healthy inventory profile.
Maintaining accurate inventory records facilitates better communication with suppliers, leading to more reliable procurement schedules and potentially favorable terms. Strong supplier relationships can result in improved quality, timely deliveries, and collaborative problem-solving.
Addressing Common Pitfalls with Smart Solutions
Challenge: Inconsistent tracking of inventory can lead to differences between recorded and actual stock levels, therefore causing stockouts or overstock conditions.
Solution: Using a cloud-based inventory management system with real-time data backup and automated inventory updates would help to centralize tracking of data. This method guarantees organizational accessibility and correctness.
Challenge: Inefficient warehouse operations, such as bad layout design and unoptimized picking procedures, can cause delays and higher labor expenses.
Solution: Identify and fix inefficiencies by tracking and reporting warehouse performance indicators including order processing speed, customer satisfaction, and inventory turnover. Warehouse management systems help simplify processes even more.
Challenge: Rapidly shifting customer demand presents a challenge in terms of either surplus or supply shortages, as both are expensive.
Solution: Develop a solid awareness of consumer wants and apply correct demand forecasting instruments. By means of this proactive technique, companies can modify inventory levels in expectation of changes in the market.
Challenge: Balancing inventory levels is difficult; excess goods raise holding costs and obsolescence risk. Insufficient stock results in missed sales opportunities and unhappy consumers.
Solution: Demand forecasting technologies that examine past sales data and market trends will help you to properly project future demand. To keep balance, define safety stock levels and reorder points.
Challenge: Without real-time tracking, companies suffer from delays in order fulfillment and an inability to react quickly to inventory problems.
Solution: Implement inventory management tools providing real-time visibility across all sales channels and storage sites. This integration improves decision-making capacity and responsiveness.
Challenge: Production halts or surplus finished items may result from inventory levels not matching production schedules, hence compromising operations and raising expenses.
Solution: Synchronize schedules by including inventory control into production planning tools. To guarantee alignment, regularly examine production plans considering present inventory data.
A Closer Look at Top IMS Solutions for Businesses
Designed for companies with complicated inventory demand, Microsoft ERP (Dynamics 365 Business Central and Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management) offers comprehensive solutions. Using AI-powered insights, it provides demand forecasts, real-time stock visibility, and automated replenishment policies. The solution easily connects with Microsoft's ecosystem, including Azure and Power BI. Additionally, it supports IoT-driven warehouse tracking, predictive maintenance, and multi-location inventory control that helps to guarantee ideal stock levels worldwide.

Designed for SMBs seeking a scalable yet reasonably priced inventory control system, Zoho Inventory is a cloud-based solution. Unlike other inventory management system software, Zoho Inventory offers flawless connection with the whole Zoho suite, including Zoho Books (accounting), Zoho CRM, and Zoho Commerce. It offers real-time stock tracking, barcode scanning, automatic purchase order generating, and multi-channel order management. Its free plan is one of its strongest points since it lets small companies track inventories without making a big initial outlay. It also provides API-based connectivity with outside apps, which helps it fit unique processes.

Designed for stores, wholesalers, and online companies needing a consistent inventory view across several sales channels, Cin7 is a connected inventory management system. Its specialties are warehouse automation, real-time stock synchronizing, and automated order routing. Companies can set automated processes to guarantee dynamic stock replenishment depending on sales patterns, hence optimizing inventory distribution.

Fishbowl helps companies to simplify production planning together with inventory tracking by offering advanced bill of materials (BOM) management, work order automation, and manufacturing execution system (MES) capability. It guarantees effective warehouse control by including barcode scanning, automatic reordering, and multi-location tracking. Its capacity to manage serialized goods and lot monitoring qualifies it for controlled sectors including food production and pharmaceuticals.

Part of Oracle's cloud ERP package, NetSuite is a very scalable inventory control system designed for mid-to-large businesses. It enables sophisticated warehouse management, therefore enabling companies to control order allocation, inventory control, and fulfillment of orders at several sites. With lot and serial tracking, the system offers end-to-end traceability and uses machine learning techniques for predictive stock forecasting.

Designed for e-commerce companies and wholesalers needing flawless connection with QuickBooks Online, QuickBooks Commerce is a multi-channel inventory and order management system. It allows consolidated inventory control among several brick-and-mortar retailers, markets, and online stores. Its automated order syncing function updates inventory in real time after every transaction, so guaranteeing precise stock levels.
QuickBooks Commerce lets companies maximize their procurement process by including purchase order automation, back-order tracking, and supplier management features as well. For companies handling perishable items, the batch and expiry tracking tools make this a strong option.

Especially strong in multi-channel e-commerce and warehouse automation, Finale Inventory is a cloud-based inventory management solution. It is quite flexible, enabling companies to fit processes for barcode-based tracking, automated stock replenishment, and order fulfillment optimization. Finale Inventory stands out mostly for its capacity to interact with QuickBooks Online, Amazon FBA, Shopify, and third-party logistics (3PL) suppliers. Its mobile barcode scanning tools also simplify warehouse operations by lowering manual mistakes and raising order processing speed.

Odoo is an open-source ERP solution offering a highly modular inventory management system. It gives companies complete power on customizing, unlike proprietary IMS systems, thereby enabling the creation of industry-specific processes. Features include automatic stock replenishment, multi-warehouse support, FIFO/LIFO inventory valuation, and demand forecasting abound. Its IoT connectivity features help companies to link RFID tags and smart sensors for instantaneous inventory control. Odoo's open-source approach makes it preferred by businesses needing custom ERP development free from vendor lock-in.

Monday presents a somewhat flexible inventory tracking system. Custom dashboards and automated workflows let companies control inventory, monitor stock movements, and link order fulfillment operations. Its drag-and-drop interface lets companies set up inventory processes without great technical knowledge.
| Competitor Name | Target Market(s) | Industry Focus | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zoho Inventory | SMB | Broad | Free plan, seamless Zoho suite integrations |
| Cin7 Limited | SMB-Mid | Retail, Wholesale, E-commerce | Industry-specific inventory solutions |
| Fishbowl | SMB | Manufacturing, QuickBooks Users | QuickBooks integration, manufacturing tools |
| NetSuite | Mid-Large | Broad ERP | Scalable inventory tracking, real-time insights |
| QuickBooks Commerce | SMB | E-commerce, Wholesale | Multi-channel order and inventory management |
| Finale Inventory | SMB | Multichannel E-commerce | QuickBooks Online integration, barcode scanning |
| Odoo | All | Broad ERP | Multi-warehouse management, automated replenishment |
| Monday.com | SMB-Mid | Customizable | Flexible inventory tracking, workflow automation |
Best Practices for a Smooth and Efficient IMS Rollout
A successful inventory stock management system implementation begins with thorough planning aligned with business objectives, like minimizing stock discrepancies, optimizing order fulfillment, or reducing carrying costs.
After planning, define your rollout that ensures smooth execution.
An IMS is only as reliable as its data. To ensure accuracy and integrity:
To maximize IMS efficiency, businesses should adopt strategic inventory control measures:
The best inventory management system is only effective if employees can use it efficiently.
How to Identify the Best Solution for Your Inventory Needs
Choosing the appropriate inventory management system is essential for simplifying operations, cutting expenses, and guaranteeing flawless supply chain activities. The market boasts several inventory control systems. You thus need a suitable solution to meet your needs regarding inventories.
Considering this, Dynamics ERP covers you. It meets your needs with two solutions: Dynamics 365 BC and Dynamics Supply Chain Management. Business Central could be a fantastic choice if you are a SMB. Its real-time inventory visibility, automatic replenishment, warehouse management, and demand forecasting driven by artificial intelligence provide Furthermore, it can integrate with Dynamics 365 ecosystem, Power BI, and third-party e-commerce platforms, which ensure seamless workflows from procurement to fulfillment.
Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management offers powerful warehouse automation, IoT-enabled tracking, and AI-powered predictive analytics for companies with multi-warehouse operations, complicated logistics, and high-volume inventory. It guarantees better end-to-end insight, cost optimization, and supply chain resiliency.